How To Find Arbitrage Bets: 4 Methods + Tips
There are four commonly used methods for identifying arbitrage betting situations.
Among them, manually searching for these opportunities is generally the most demanding in terms of time and attention.
Each method comes with its own advantages and limitations, depending on experience level, available tools, and market access.
In addition to the core methods described below, it is important to review the accompanying practical considerations and cautions before attempting to apply them in real betting environments.
To look for arbitrage opportunities, bettors typically rely on one of the following approaches:
- Comparing odds manually
- Using free odds-comparison websites
- Using paid arbitrage scanner software
- Developing a custom odds-scanning solution
1. Manual odds comparison
Manually identifying arbitrage opportunities is generally the most complex and least efficient approach for most bettors.
One advantage of this method is that it does not require paying for an odds-comparison service.
However, manual arbitrage searching is extremely time-consuming and often impractical without adequate hardware, such as a fast computer and multiple monitors, as well as the ability to react quickly to changing odds.
To compare odds manually, bettors typically open the same sporting event across multiple bookmakers in separate browser tabs.
A significant limitation of this method is that bookmakers have improved their pricing algorithms and now adjust incorrect or exposed odds much faster than in the past.
Between 2010 and 2015, manually identifying arbitrage situations was more feasible because odds updates occurred more slowly.
During that period, bookmakers made pricing errors more frequently, allowing bettors additional time to react.
Today, manual comparison can still occasionally reveal opportunities, particularly when comparing slower local bookmakers against more efficient or arbitrage-friendly sportsbooks.
As more bettors use scanners and automated tools, price discrepancies tend to be corrected faster, reducing the frequency and size of available arbitrage margins.

For beginners, this means that manually finding meaningful discrepancies has become increasingly difficult.
One advantage of manual searching is that not all bookmakers and markets are included in scanner databases.
Understanding which bookmakers are not widely scanned may marginally increase the chance of spotting inconsistencies.
How to find arbitrage opportunities manually
To search manually, bettors must open the same sporting event at multiple bookmakers, ideally across two screens, and compare markets and outcomes individually.
Start by identifying bookmakers available in your jurisdiction that have an established reputation for reliability.
Check whether these bookmakers are included in popular arbitrage scanners.
Choose a sport you understand reasonably well. For beginners, football and tennis are often easier due to market familiarity and liquidity.
Compare identical markets across bookmakers, focusing on simple two-outcome markets first.
These include over/under goals, corners, or cards.
If you are familiar with handicap markets, these can also be reviewed.
For manual searching, tennis markets often provide clearer pricing comparisons when matched against sharp bookmakers.
To assist with calculations, free arbitrage calculators are widely available online.
In practice, live betting markets may present more frequent pricing discrepancies, but they also carry higher execution risk.
Prediction market arbitrages can also emerge under specific conditions, though they require additional understanding.
Manual arbitrage in live events
To attempt manual arbitrage during live events, the following considerations apply:
Markets that move quickly can occasionally present brief pricing inconsistencies, but they also carry a higher likelihood of odds changing before bets are placed.

Common football markets include over/under goals, corners, handicaps, and disciplinary markets.
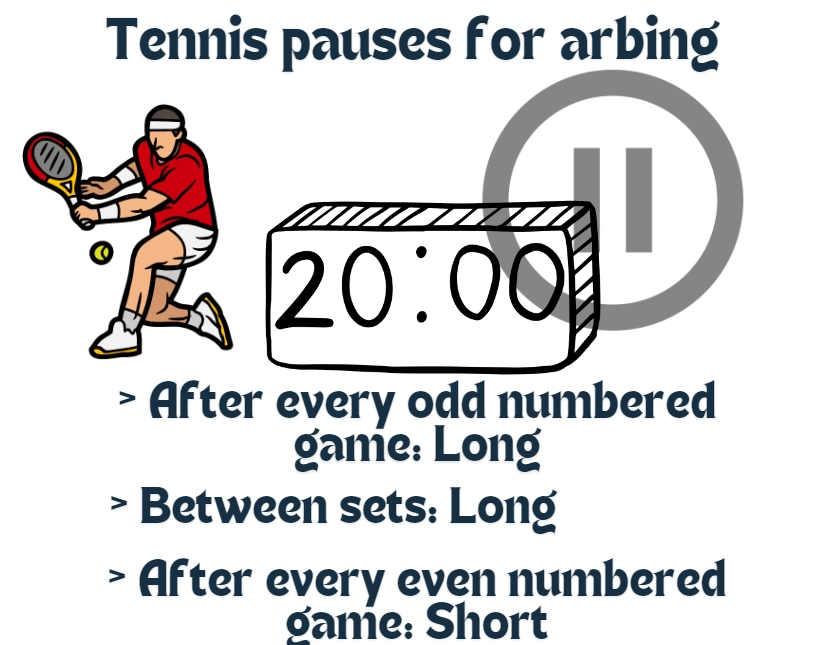
For tennis, over/under games, handicaps, and set winners are commonly observed. Waiting for breaks in play can reduce execution risk.
These precautions help limit exposure when markets move unexpectedly.
Basketball arbitrage often involves totals, handicaps, and quarter or half markets, though similar risks apply.
Live arbitrage generally requires significant experience due to rapid odds movement.
While opportunities may exist, they are often short-lived and prone to execution errors.
For beginners, using structured tools is usually more practical than manual live searching.
2. Using free odds-comparison sites
Free arbitrage scanners are often the most accessible option for beginners.
These services typically scan bookmakers at fixed intervals, with slower refresh rates than paid tools.
Advantages of free scanners
- Allows users to learn arbitrage concepts without upfront cost
- Faster opportunity discovery compared to manual searching
- Helps identify which bookmakers align with individual needs
- May assist with completing bonus wagering requirements

Disadvantages of free scanners
- Profit margins are usually capped, often between 1% and 3.5%
- Delays of up to one minute are common
- Many users monitor the same opportunities, accelerating odds corrections
- Some opportunities disappear before execution
In markets with many bookmakers, such as the UK, focusing only on very small arbitrage margins may be inefficient.
Finding opportunities before odds adjust
To identify opportunities earlier, faster-updating software is generally required.
Some free tools can still be useful for monitoring markets, but they are rarely sufficient for consistent execution.
Limited free trials from premium services can provide temporary access to faster data with restricted margins.
While these trials may still limit profit percentages, they allow users to observe how paid tools function.
To consistently detect opportunities before price corrections, paid services are typically required.
Paid tools differ in update speed, bookmaker coverage, and filtering options.


3. Using paid arbitrage scanner software
Paid arbitrage scanners generally provide more timely and comprehensive market coverage.
These tools typically remove delays and profit caps present in free versions.
With paid access, users can see opportunities closer to the moment they appear.
The primary advantage of premium scanners is execution speed, which can reduce the likelihood of odds changing mid-bet.
Relying solely on free tools can limit scalability, as execution delays increase with market competition.
Paid services do not eliminate risk but can improve operational efficiency when used carefully.
4. Developing custom arbitrage software
Building a proprietary arbitrage scanner is technically demanding and carries a high failure rate.
Many developers underestimate the complexity of data acquisition, latency, and bookmaker restrictions.
Developing a functional tool typically requires:
- Advanced programming skills
- A strong understanding of arbitrage mechanics
- Access to reliable, low-latency odds data
- Extensive development and testing time
In most cases, developing a private scanner is not cost-effective without access to premium data feeds.
Low-cost APIs often update too slowly to remain competitive.
Custom solutions may be viable only with significant technical resources and infrastructure.
Practical steps for identifying arbitrage opportunities
1. Compile a bookmaker list
Identify reputable bookmakers available in your jurisdiction.
Since arbitrage strategies are often restricted, reliability is essential.
2. Access sharp or exchange pricing
Using at least one bookmaker or exchange with higher limits helps offset exposure.
This reduces execution risk and stake restrictions.
3. Configure filters carefully
Limit scans to bookmakers where funds are available.
Start with basic sports and markets before refining filters.
4. Prioritize stable opportunities
Avoid discrepancies that appear for only a fraction of a second.
Short-lived signals often reflect data delays rather than true pricing gaps.
5. Calculate stakes accurately
Use built-in calculators to determine proportional stakes.
Fixing one side of a bet helps manage exposure at slower bookmakers.
6. Execute cautiously
Double-check markets, odds, and stakes before confirming bets.
Odds changes can force hedging at a loss if execution is delayed.
7. Manage mistakes conservatively
Execution errors are inevitable.
Accepting a controlled loss is often preferable to leaving exposure unhedged.
8. Start with low stakes
Limited capital should be deployed gradually.
Small bonuses and low stakes reduce operational stress.
9. Avoid drawing attention
Large or highly visible arbitrage positions may trigger account restrictions.
Lower-margin bets can reduce detection risk.
Final note
Arbitrage betting involves operational complexity, execution risk, and account limitations.
This guide is intended to explain how arbitrage opportunities are identified—not to guarantee outcomes.
Actual results depend on timing, market conditions, and individual execution discipline.
